Second year groups were asked to produce a 1:20 detailed section model of their construction pack which was provided by another group in the year. The objective of the project was to use the model to demonstrate their understanding of the buildings construction in terms of its technical details, services and environmental performance.
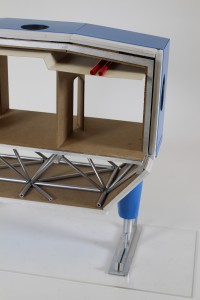
This groups building, known as ‘Halley 6’ is the British Antarctica research station. The chosen section featured two supporting legs and look at internal structural elements in relation to the outer facade as well as ducting voids.
The submission was given in alongside a report including a 3D Digital structural model that also showed the main structural components.
The model was made using plastic tubing for structural space frame components, vac forming plastic sheets to form the leg supports and clad the exterior. In order to make the leg shape a former was made to wrap the plastic around which was heated and glued into shape. The leg assembly and skis were represented with laser cut elements that were spray painted. Flooring and interior walls were made using 3mm MDF.




















































 Last week 2nd year students were given the task of further refining their designs for structural elements. By taking their initial ideas to the next stage they came up against many more problems to solve in particular how joining replicated components would work in practice as they made seven identical units to work with one another towards supporting a structure or forming a building form.Â
Last week 2nd year students were given the task of further refining their designs for structural elements. By taking their initial ideas to the next stage they came up against many more problems to solve in particular how joining replicated components would work in practice as they made seven identical units to work with one another towards supporting a structure or forming a building form. 






 Marco Wan had an interesting approach to creating the curved planes for his design. This process is called ‘glulam’ and as the name hints at, involves laminating sheets together with layers of glue and material whilst clamped in a given shape. This produced a very strong formed shape that can and is used for many 1:1 building applications. Very nice to see a student employing this technique in their model development.
Marco Wan had an interesting approach to creating the curved planes for his design. This process is called ‘glulam’ and as the name hints at, involves laminating sheets together with layers of glue and material whilst clamped in a given shape. This produced a very strong formed shape that can and is used for many 1:1 building applications. Very nice to see a student employing this technique in their model development.


























